How to Build Cloud-Native Apps with Java Technologies?
Explore contemporary Java technologies for building modern cloud-native applications, ranging from microservices to serverless architectures. Uncover best practices and essential tools.

Cloud-native applications are specifically designed for cloud computing environments, leveraging containerization, microservices, and serverless architectures to create scalable, resilient, and easily deployable solutions. These applications can be developed and updated more rapidly by following modern development and operation methods, such as continuous integration and deployment.
Java is a popular programming language for cloud-native applications, thanks to its portability, versatility, and rich ecosystem. Java provides a wide range of tools, libraries, and frameworks, along with crucial features like interoperability, scalability, and backwards compatibility, making it a suitable choice for building cutting-edge cloud-native applications.
Java Microservices Frameworks
Microservices have become a mainstay in modern software development, enabling organizations to build large, complex applications by breaking them down into smaller, manageable, and independent services. Each service is responsible for a specific business capability and communicates with other services through APIs, allowing developers to build, deploy, and scale services independently. Java offers several popular microservices frameworks to make building these applications more accessible and efficient.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot is a widely-used Java framework that simplifies the development and deployment of microservices. It provides essential tools and preconfigured templates to build stand-alone, production-ready applications without tedious boilerplate code. Spring Boot's cloud-native capabilities include features like embedded containers, externalized configuration, and health endpoints that help developers build resilient cloud-native applications.
Quarkus
Quarkus is a modern Java framework that aims to optimize both development and runtime aspects, making it suitable for cloud-native environments. Quarkus improves startup time, reduces memory footprint, and lowers the operational cost of applications. Its cloud-native capabilities include container readiness, serverless optimization, and advanced support for both imperative and reactive programming paradigms.
Vert.x
Vert.x is a lightweight Java framework for building high-performance, non-blocking, and event-driven applications. Its reactive nature allows developers to create applications that can handle high concurrency, making it efficient and scalable for cloud-native deployments. Vert.x offers polyglot support, letting developers write code in multiple languages, such as Java, Kotlin, JavaScript, Scala, and Groovy.
Micronaut
Micronaut is another Java microservices framework, focusing on minimal overhead and ease of development. It provides the necessary features for creating microservices and serverless applications, such as dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and configuration management. Micronaut optimizes application startup time and memory consumption, making it suitable for cloud-native environments.
Serverless Architectures in Java
Serverless computing is a rapidly growing approach to cloud-native architecture, allowing developers to build and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. These applications are structured into small, single-purpose functions that execute on-demand in response to events, resulting in cost-effective and highly scalable solutions. Java developers can leverage serverless architectures using various tools and platforms that support Java.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing platform provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), supporting Java as one of its languages. Java developers can write Lambda functions using the AWS Lambda Java runtime and access AWS resources and other services. AWS Lambda takes care of managing, scaling, and patching the underlying infrastructure, enabling Java developers to focus on writing code.
Google Cloud Functions
Google Cloud Functions is a serverless computing platform from Google Cloud, supporting Java as a first-class language. Java developers can write functions using the lightweight Java 11 runtime offered by Google Cloud Functions, which provides a simple API to respond to events and process data. Like AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions abstracts away infrastructure management, allowing developers to work on business logic.
Azure Functions
Azure Functions is Microsoft's serverless computing service, which also supports Java. Java developers can write and deploy functions using standard Java development tools, such as Maven, Gradle, and Visual Studio Code. Azure Functions integrate seamlessly with other Azure services and third-party applications, enabling Java developers to build scalable and resilient serverless applications while focusing on code, not infrastructure management.
Containerization and Java
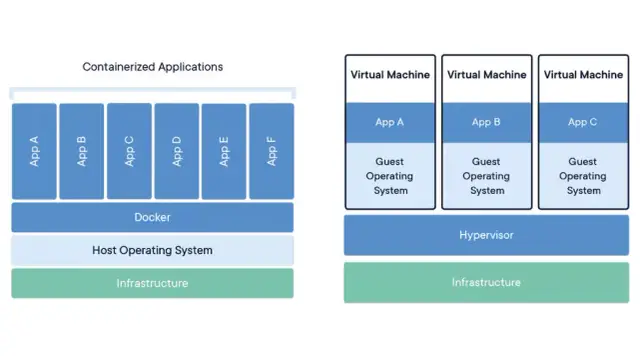
Containerization has emerged as a popular technology for packaging and distributing applications, ensuring they run consistently across different environments. For Java-based cloud-native applications, containerization offers the following benefits:
- Lightweight and portable environments: Containers bundle application code, libraries, and dependencies into a single unit, ensuring consistency and efficiency when running applications across diverse infrastructure and platforms.
- Resource efficiency: As containers run on the same host operating system and share the same resources, they're more resource-efficient than running multiple virtual machines.
- Ease of scaling and orchestration: With containerization, developing, scaling, and orchestrating cloud-native applications becomes easier and more efficient.
To leverage containerization, Java developers can use several tools and technologies. Two of the most popular include Docker and Kubernetes.
Docker
Docker is an open-source platform for automating the development, deployment, and management of applications within containers. With Docker, Java developers can build lightweight, portable, and reproducible container images that can be shipped to any environment. Docker provides several advantages for Java developers:
- Efficient builds: Developers can author Dockerfiles to build and configure Java application images, ensuring consistent steps and minimal dependencies.
- Application isolation: Docker containers isolate Java applications, preventing conflicts with other applications or system packages.
- Multi-platform support: Docker containers can run on any platform, provided the underlying host system supports the Docker runtime.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source orchestration platform for managing containerized applications. It automates the deployment, scaling, and management of cloud-native Java applications built using microservices architectures. Kubernetes offers several benefits to Java developers building cloud-native applications:
- Automated scaling: Kubernetes can automatically scale Java applications based on resource usage or custom metrics.
- High availability: Kubernetes ensures applications are resilient to failures by managing and distributing replicas across multiple nodes.
- Rolling updates and rollbacks: Kubernetes supports rolling updates and rollbacks for Java applications, allowing developers to deploy new features without downtime. By leveraging containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes, Java developers can simplify the deployment, scaling, and management of their cloud-native applications.
Java Cloud Platform Providers
Major cloud platform providers offer various services that facilitate the development, deployment, and maintenance of Java-based cloud-native applications. Some of the popular Java cloud platform providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides a range of services for running Java applications, including AWS Lambda for serverless computing, Amazon Elastic Beanstalk for platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and Amazon EC2 for infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS). AWS also offers managed services for Java frameworks, such as AWS Corretto for running OpenJDK applications.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP offers services for deploying, monitoring, and scaling Java applications, including Google App Engine (PaaS), Google Compute Engine (IaaS), and Google Kubernetes Engine for container orchestration. GCP also provides Cloud Functions for creating serverless Java functions.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure supports Java application development with services like Azure Functions (serverless), Azure App Service (PaaS), and Azure Kubernetes Service for container orchestration. Azure also integrates with popular Java tools, frameworks, and libraries to streamline the development process.
- Oracle Cloud: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides services and tools for running Java applications, such as Oracle Java Cloud Service for running WebLogic Server applications, Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes, and Oracle Cloud Functions for serverless computing.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud offers various services for Java developers, including IBM Cloud Foundry for platform-as-a-service solutions and IBM Kubernetes Service for container orchestration. IBM Cloud also supports Java serverless computing with Apache OpenWhisk. These Java cloud platform providers offer an extensive range of tools, services, and support to help developers build and manage cloud-native Java applications.
Java-based CI/CD and Automation
A continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) pipeline is essential for the rapid development and release of Java-based cloud-native applications. Java has various tools and technologies that facilitate efficient CI/CD and automation.
- Jenkins: Jenkins is an open-source automation server that enables Java developers to automate the build, test, and deployment processes. Jenkins supports numerous plugins, integrations, and extensibility options to adapt to various development workflows.
- Maven and Gradle: Both Maven and Gradle are popular build automation tools for Java applications. Maven follows a standard project structure and relies on XML configuration, while Gradle offers a flexible Groovy or Kotlin-based DSL for build scripts. Choosing between these tools depends on developers' requirements and preferences.
- Git: Git is a widely-used version control system that facilitates code collaboration, branching, and merging. Java developers can track and manage their source code in a centralized or distributed manner, ensuring smooth codebase management across teams.
- JUnit and TestNG: JUnit and TestNG are testing frameworks for Java applications, enabling developers to write and execute unit and integration tests. These frameworks help ensure the quality and reliability of Java-based cloud-native applications.
- Code coverage tools: JaCoCo and Cobertura are widely used for Java applications. They help developers monitor code coverage metrics during the build and testing processes, enabling the identification of areas that need improvement.
- Monitoring and performance tools: Monitoring and performance tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK Stack help developers monitor Java application performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resource usage in cloud environments. Incorporating Java-based CI/CD and automation tools into the development process can streamline the creation, testing, and deployment of cloud-native Java applications, ensuring scalable, and performant software.
AppMaster: No-Code Platform for Rapid Development
In the ever-evolving world of cloud-native app development, no-code platforms have become a game-changer. Among these, AppMaster is a powerful no-code tool for simplifying the development process. It caters to developers and businesses seeking a swift and efficient way to create applications without extensive coding skills.
Simplifying Development with No-Code Tools
AppMaster offers a user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface that simplifies the app development. Developers and even non-technical team members can leverage its intuitive tools to build, modify, and iterate on applications swiftly. The platform streamlines the creation of various app components, from user interfaces to data integrations, making it accessible and efficient for a wide range of users.
AppMaster's Role in Cloud-Native App Development
In the realm of cloud-native app development, AppMaster contributes significantly to the rapid creation of applications. Its no-code approach ensures that businesses can keep up with the dynamic requirements of cloud-native environments. As cloud-native apps rely on flexibility, scalability, and continuous delivery, AppMaster's capabilities empower developers to adapt to these needs quickly and precisely. With AppMaster, cloud-native apps can be brought to life more swiftly, facilitating businesses' transitions to the cloud-native sphere.
Final Thoughts
Developing cloud-native applications with Java technologies has become a popular approach due to the vast ecosystem of tools, frameworks, and cloud platforms available. By utilizing Java's frameworks, architectures, and services, developers can build scalable, interoperable, and powerful applications tailored to modern cloud environments. When selecting the right combination of Java technologies for your cloud-native applications, it's essential to evaluate the specific requirements and goals of your project.
Choosing an appropriate microservices framework, opting for a serverless architecture when required, and leveraging containerization and automation are crucial steps in the process. Moreover, it's essential to know the various cloud platform providers and the specific services they offer for Java applications.
Java remains a strong choice for building cloud-native applications due to its diverse features, tools, and powerful ecosystem. By embracing contemporary Java technologies, developers can ensure their applications are well-suited to modern, cloud-based environments and deliver scalable, maintainable, and efficient solutions.
FAQ
Cloud-native applications are developed specifically for cloud environments, designed using microservices architectures, and can easily be scaled, deployed, and updated using modern development and operation methodologies.
Java provides a wide range of tools, frameworks, and libraries, along with features like interoperability, scalability and backwards compatibility, that facilitate the development of cloud-native applications.
Java microservices frameworks include Spring Boot, Quarkus, Vert.x, and Micronaut, which offer a range of capabilities like container readiness, development speeds, and resource efficiency.
Java developers can leverage serverless architectures using tools like AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions, which enable running Java functions as a service without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Containerization provides lightweight, portable, and isolated environments for various Java application components, allowing them to run with consistency in the cloud. Tools like Docker and Kubernetes help in managing the deployment and scaling of these containers.
Java cloud platform providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, and IBM Cloud, which offer various tools and services for deploying, monitoring, and maintaining Java applications in the cloud.
Java-based CI/CD pipelines include tools like Jenkins, Maven, Gradle, and Git for automating the build, test, and deployment of applications, as well as monitoring features to ensure reliability and performance.





