Understanding the Differences: Zerocode, Low-Code, and Traditional Coding
Get an in-depth understanding of the differences between Zerocode (No-Code), Low-Code, and Traditional Coding platforms. Learn their pros, cons, and use cases in different industries and how they benefit innovation and business growth.

The software development industry is evolving rapidly, offering organizations a range of development platforms and methodologies designed to optimize the process and fulfill their specific needs. These platforms can be broadly classified into three major categories: Zerocode ( No-Code), Low-Code, and Traditional Coding. In this article, we will explore these three categories and highlight their key differences and use cases in different industries.
Zerocode (No-Code) Platforms
Zerocode, or No-Code development platforms, are designed to empower non-technical users to create applications, websites, and other software solutions without having to write any code. With a visual, drag-and-drop interface, users can design components and visually define application processes, allowing them to build fully functional applications quickly and easily.
No-Code platforms enable anyone with an idea to transform it into a working product, considerably lowering the barriers to entry for software development. The No-Code movement has gained significant momentum in recent years, as businesses and entrepreneurs search for more efficient, accessible ways to create software solutions. Some popular examples of No-Code platforms include AppMaster.io, Wix, Bubble, and Webflow.
Key Features of Zerocode Platforms
- Visual Interface: Zerocode platforms provide a simple drag-and-drop interface for designing and building applications, minimizing or entirely eliminating the need for any coding.
- Rapid Application Development: Zerocode platforms enable users to create functional applications quickly, which is ideal for businesses with tight deadlines or limited resources.
- User-Friendly: Designed for users without programming knowledge, Zerocode platforms are highly intuitive and accessible for non-technical users.
- Low Technical Risk: With no-code solutions, debugging, maintenance, and updating are typically more straightforward than coding-dependent platforms, reducing technical risk and project complexity.
Low-Code Platforms
Low-Code platforms fall somewhere between No-Code platforms and Traditional Coding methods. They provide a quicker development process compared to traditional coding methodologies while retaining some degree of customization and flexibility. These platforms allow users to create software solutions faster, with a visual drag-and-drop interface for designing software components while also permitting customization through coding for additional flexibility.
Low-Code platforms cater to a wide range of user skill levels, from non-technical users to developers looking to accelerate their software development process. Some examples of Low-Code platforms include OutSystems, Mendix, and Appian.
Key Features of Low-Code Platforms
- Visual Drag-and-Drop Interface: Low-Code platforms provide users with a visual interface to design and compose applications, simplifying the development process and reducing the time required.
- Code Customization: While Low-Code platforms primarily rely on visual tools, they still allow for code customization, achieving a balance between ease-of-use and development flexibility.
- Faster Development Times: By combining visual tools with the ability to write custom code, Low-Code platforms can expedite the development process and produce applications in a fraction of the time compared to traditional coding methods.
- Bridging the Skill Gap: Low-Code platforms cater to a variety of skill levels, making them suitable for both non-technical users and experienced developers who seek to accelerate their development process.
Traditional Coding Platforms
Traditional Coding, also known as hand-coding, is the process of creating software applications, websites, and other solutions through the manual writing of code, from scratch, in various programming languages like Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript. Developers following this approach must possess an in-depth knowledge of the technologies, libraries, and frameworks that are required to build the desired solution.
Traditional Coding is often the default choice for many businesses and developers, especially when it comes to creating custom, complex software solutions. However, this approach may be time-consuming and expensive.
Features of Traditional Coding Platforms
Traditional Coding platforms typically have several key features that set them apart from Zerocode and Low-Code alternatives:
- Complete customization: Traditional Coding allows developers to create highly customized and unique solutions tailored to specific business requirements.
- Exclusively code-based: With Traditional Coding, developers must write all code manually, following structured programming languages and incorporating various frameworks, libraries, and tools.
- Higher learning curve: Extensive knowledge of various programming languages, methodologies, and technical concepts is essential for developers working with Traditional Coding platforms.
- Longer development time: As every component and functionality is customized and coded from scratch, the time required to complete projects using Traditional Coding is usually higher compared to Zerocode and Low-Code alternatives.
Comparison of Zerocode, Low-Code, and Traditional Coding
The primary differences between Zerocode (No-Code) platforms, Low-Code platforms, and Traditional Coding platforms lie in their approach to development, target user base, and levels of customization allowed. Here's an overview of their key differences:
- Development approach: Zerocode platforms rely on visual drag-and-drop interfaces for designing and building software, removing the need for code altogether. Low-Code platforms provide a similar visual interface but offer the option for additional customization using code. Traditional Coding requires developers to manually write code using various programming languages.
- Target user base: Zerocode platforms are designed for non-technical users, such as citizen developers and business analysts, who can build applications without coding knowledge. Low-Code platforms cater to a wider range of users, including both non-technical users and experienced developers. Traditional Coding is suitable for highly skilled developers with in-depth knowledge of various programming languages, methodologies, and frameworks.
- Customization: Zerocode platforms offer pre-built components and limited customization options, while Low-Code platforms enable developers to extend and customize components through coding. Traditional Coding provides complete control and maximum customization, allowing developers to create highly tailored solutions.
Pros and Cons
Each of these development approaches has its advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore the pros and cons of Zerocode (No-Code), Low-Code, and Traditional Coding platforms:
Zerocode (No-Code) Platforms
Pros:
- Rapid development time, significantly reducing time to market
- Cost-effective, as it requires fewer development resources
- Accessible to non-technical users, expanding the pool of potential application creators
- Lower technical debt and simplified maintenance, debugging, and upgrades
Cons:
- Limited customization and flexibility, as users are restricted to pre-built components and templates
- Potential vendor lock-in, since applications are heavily dependent on the specific Zerocode platform
- May not be suitable for complex, unique, or highly specialized solutions
Low-Code Platforms
Pros:
- Faster development time compared to Traditional Coding, while retaining the benefits of code customization
- Suitable for a wide range of user skill levels, including non-technical users and experienced developers
- Better suited for custom solutions than Zerocode platforms, thanks to their mix of visual tools and coding capabilities
Cons:
- May still impose limitations on customization compared to Traditional Coding
- A higher learning curve for non-technical users than Zerocode platforms
Traditional Coding Platforms
Pros:
- Complete control over customization, allowing developers to create unique and highly specialized solutions
- Wide range of programming languages, methodologies, and frameworks available for use
Cons:
- Slower development times and higher costs due to the need for experienced developers and resources
- Requires extensive knowledge in programming languages and various technologies, which leads to a higher learning curve
Ultimately, the choice of platform depends on factors like the level of customization required, time and resource constraints, target audience, and the level of technical expertise available within a business or development team.
Zerocode, Low-Code, and Traditional Coding: The Verdict
The choice between Zerocode (No-Code), Low-Code, and Traditional Coding platforms depends on your specific use case, requirements, budget, and available resources. Each development approach caters to different needs and industries. Zerocode platforms have grown in popularity due to their ability to democratize and expedite the application development process.
Non-technical users can create applications, websites, and other software solutions without learning how to code. This makes Zerocode platforms particularly suitable for small businesses and startups looking for cost-effective ways to create solutions quickly. On the other hand, limited customization and flexibility could be a drawback in some scenarios.
Low-Code platforms bridge the gap between Zerocode and Traditional Coding, enabling a faster development process compared to traditional methods while still providing customization capabilities. Low-Code platforms are suitable for businesses and organizations that require more tailor-made solutions, have some in-house coding experience, and want to strike a balance between ease of use and flexibility. However, there might be limitations in customization when compared to traditional coding.
Traditional Coding remains important for creating highly specialized solutions that require the unique abilities and expertise of professional developers. Although this approach takes longer and requires higher technical expertise, it offers the highest level of customization and flexibility. This makes it suitable for large enterprises and organizations that have more complex and specific requirements. In summary, the choice between Zerocode, Low-Code, and Traditional Coding depends on factors such as:
- Scope and complexity of the project
- Customization and flexibility requirements
- Skill level of the team
- Budget and resources
- Implementation and maintenance costs 6. Speed of development and updates
Consider these factors and weigh the pros and cons for each approach to make the best choice for your project.
AppMaster: A Leading No-Code Platform Example
AppMaster.io is a prime example of a powerful no-code platform designed to streamline and simplify application development. Founded in 2020 and with over 60,000 users as of April 2023, AppMaster delivers an end-to-end solution for creating backend, web, and mobile applications without writing a line of code.
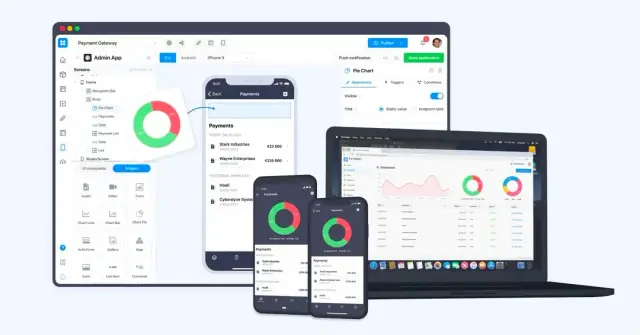
AppMaster allows users to create applications with rich functionality, including data models, business logic, REST APIs, and web sockets. AppMaster generates source code for applications, compiles them, runs tests, and deploys to the cloud, ensuring seamless integration of your user interface, backend, and mobile applications with real-time updates and no technical debt. Highlighted on G2 as a High Performer and Momentum Leader in No-Code Development Platforms, AppMaster is ideal for a wide range of users, from small businesses to large enterprises.
With its Learn & Explore free tier to its specialized Business+ and Enterprise subscriptions, AppMaster offers versatile plans to cater to varying needs. AppMaster continues to pioneer the no-code revolution, providing an accessible and efficient way for users to bring their ideas to life without the complexities of traditional coding. Its focus on eliminating technical debt, reducing development time, and lowering costs make it a standout platform in the world of no-code development. Learn more about AppMaster.io and its features by signing up for a free account.
FAQ
Zerocode or No-Code platforms are development tools that empower non-technical users to create applications, websites, and other software solutions using a visual, drag-and-drop interface without writing any code.
Low-Code platforms are development tools that help users create software solutions faster than traditional coding methods, as they involve a visual drag-and-drop interface for designing software, while still allowing for customization through coding.
Traditional Coding refers to the conventional development process, where developers create applications and other software solutions by writing code in various programming languages.
Zerocode platforms do not require any coding knowledge, while Low-Code platforms allow for code customization but still use visual tools to expedite the development process. Traditional Coding platforms require extensive coding knowledge and follow a step-by-step development process.
Zerocode platforms offer advantages such as speed of development, cost-effectiveness, ease of use for non-technical users, and low technical risk in regards to maintenance, upgrades, and debugging.
Disadvantages of Zerocode platforms include limitations in customization, less flexibility compared to traditional coding and low-code platforms, and potential vendor lock-in.
Low-Code platforms provide a faster development process compared to traditional coding, while still retaining the flexibility of customization through code. They also cater to a wider range of user skill levels, from non-technical users to experienced developers.
Disadvantages of Low-Code platforms include potential limitations in customization and a higher learning curve compared to Zerocode platforms.
Traditional Coding platforms offer complete customization and flexibility, supporting a wide range of languages and technologies. This allows developers to create unique and highly specialized solutions.
Disadvantages of Traditional Coding platforms include slower development times, a higher learning curve, and a higher cost due to the need for experienced developers and resources.