User Experience (UX) Design
Learn about the principles and strategies of User Experience (UX) Design to improve the usability and satisfaction of your website or app's users.

As we navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape, the importance of User Experience (UX) Design has become increasingly apparent. Whether you're creating a website or app, how users interact with your product can make or break their experience. From first impressions to intuitive navigation, every aspect of your digital product plays a critical role in determining its success. That's why UX Design is essential for creating a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
UX Design is not just about making a website or app look good, and it's about understanding the needs and behaviors of your users and creating a product that meets those needs in the most intuitive way possible. It's a process that involves research, testing, and iterative design to ensure that the final product is not only visually appealing but also easy to use and navigate.
In this article, we'll take a deep dive into the principles and strategies of UX Design. We'll explore the key elements that make up a great user experience, such as usability, accessibility, and engagement. We'll also show you how to use research and testing to understand your users better and create a product that meets their needs. Whether you're a designer, developer, or business owner, you'll learn how to use UX Design to improve the usability and satisfaction of your users.
What is User Experience (UX) Design?
User Experience (UX) Design is designing and developing digital products such as websites and apps to provide users with a seamless and enjoyable experience. It encompasses the complete procedure of obtaining and incorporating a product, including design, usability, function and branding. UX Designers use various techniques, such as user research, prototyping, and testing, to understand the needs and behaviors of users and create a product that meets those needs in the most intuitive way possible. The ultimate goal of UX Design is to create a product that is easy to use, accessible, and engaging for users.
Why should you care about UX?
Understanding the importance of User Experience (UX) Design is crucial for creating digital products that meet the needs and expectations of users. A well-designed product with a seamless and enjoyable user experience can lead to several benefits for your business or organization.
Firstly, you can improve user satisfaction and engagement by designing a product with user needs and behaviors. This can lead to increased conversions, as users are more likely to complete desired actions, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. Additionally, a positive user experience can lead to increased loyalty and repeat usage of your product.
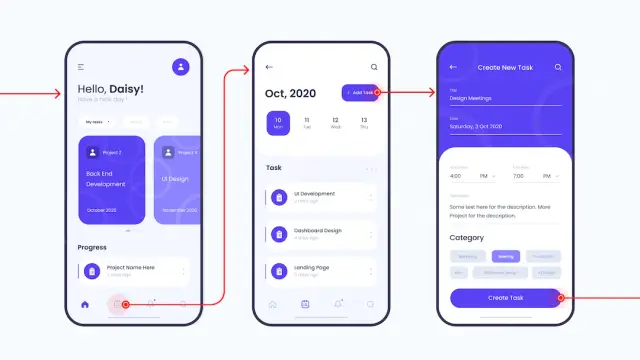
Investing in UX Design at the beginning of the software development process can also be cost-effective. By identifying and addressing potential usability issues early on, you can save time and money in the long run. Furthermore, having a superior user experience compared to your competition can be a key differentiator that can set your product apart in the market.
Lastly, it's important to mention that accessibility is a fundamental part of UX design, which means designing for users with disabilities. This not only makes your product more inclusive, but it also complies with legal requirements in some countries.
UX Design is about understanding the needs and behaviors of your users and creating a product that meets those needs in the most intuitive way possible. By caring about UX, businesses and organizations can benefit from improved user satisfaction, increased conversions, increased loyalty, cost-effective development, and competitive advantage, not to mention compliance with accessibility laws.
The role of the UX designer
The role of a User Experience (UX) designer is to design and develop digital products such as websites and apps to provide a seamless and enjoyable experience for users. This includes conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, and testing the product to ensure that it meets the users' needs.
The UX designer's responsibilities include the following:
- User research includes conducting interviews, surveys, and usability testing to understand the needs and behaviors of the users.
- Creating wireframes and prototypes: Using the information gathered from user research, the UX designer creates wireframes and prototypes that demonstrate the overall structure and layout of the product.
- Testing the product: The UX designer conducts usability testing to ensure that the product is easy to use and navigate and meets the users' needs.
- Collaborating with cross-functional teams: UX designers often work closely with other team members, such as developers, product managers, and stakeholders, to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the users and the business.
- Keeping up to date with industry trends and best practices: The role of a UX designer is constantly evolving, and they need to stay up to date with the latest trends, tools, and best practices in the industry.
- Accessibility: UX designers should also consider accessibility guidelines and inclusive design principles to ensure that the product is usable by people with disabilities.
The role of a UX designer is to create digital products that are easy to use, accessible, and engaging for users by understanding their needs and behaviors and by testing and iterating the design to ensure that it meets those needs.
Tools and techniques of UX
User Experience Design is a complex process involving various tools and techniques to design and develop digital products, such as websites and apps, that provide users with a seamless and enjoyable experience. In addition to the tools and techniques mentioned previously, here are some additional tools and techniques that UX designers may use:
- Card sorting: A technique used to understand the organization and labeling of content and to identify the most intuitive and meaningful categories for users.
- Affinity mapping: A technique used to organize and make sense of qualitative data, such as user research findings and feedback.
- Remote usability testing: A technique used to conduct usability testing remotely, allowing the designer to test the product with users in different locations.
- Interactive prototyping: A technique used to create interactive prototypes that simulate the behavior and functionality of the final product.
- Design thinking: A problem-solving approach that emphasizes empathy, experimentation, and iteration in the design process.
- User flow diagrams: A technique used to map out a user's steps to complete a task on a website or app and identify potential usability issues.
- Usability heuristics: A set of guidelines and best practices used to evaluate a product's usability.
- User feedback platforms: A tool that allows users to provide feedback on the product and to rate the usability, design, and overall experience.
- Eye-tracking heat maps: A tool that tracks and analyzes where users are looking on a website or app and understands their visual attention.
- Voice user interface (VUI) design: A technique used to design voice-enabled products such as Amazon Echo, Google Home, and voice assistants on mobile devices.
These tools and techniques help UX designers to research, design, prototype, test, and evaluate digital products, allowing them to create easy-to-use, accessible, and engaging experiences for users.
What are the differences between UX and UI design?
UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design are two distinct but related disciplines that focus on creating digital products such as websites and apps. While both UX and UI design plays a critical role in determining the success of a digital product, they have different goals and focus on different aspects of the design process.
UX design is primarily concerned with the overall experience of the user. It focuses on understanding the needs and behaviors of the users and designing a product that meets those needs in the most intuitive way possible. This includes conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, and testing the product to ensure that it is easy to use and navigate.
On the other hand, UI design is primarily concerned with the aesthetic and interactive elements of the product. It focuses on creating a visually appealing, consistent design that guides the user through the product. This includes choosing colors, typography, and imagery and designing buttons, forms, and other interactive elements.
In summary, UX design is about creating a product that is easy to use and meets the users' needs, while UI design is about creating a visually appealing product that guides the user through the product. While both UX and UI design is essential, they have different goals and focus on different aspects of the design process. They work together to create a cohesive and effective experience for the users.
User Experience Design (UX) and no-code
User Experience (UX) design is a crucial aspect of creating digital products that are both functional and enjoyable to use. UX design aims to create products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users, making their interactions with the product as seamless and satisfying as possible. With the proliferation of no-code solutions, it has become easier for businesses and individuals to create their own digital products without extensive coding knowledge.
No-code solutions such as website builders, drag-and-drop interfaces, and automation tools allow users to quickly and easily design and create digital products that are tailored to their specific needs. This democratization of design and development has made it possible for more people to create products that meet the needs of their users, leading to improved overall user experience. Additionally, these tools often come with pre-designed templates and components that can be easily customized to create a polished and professional-looking product.
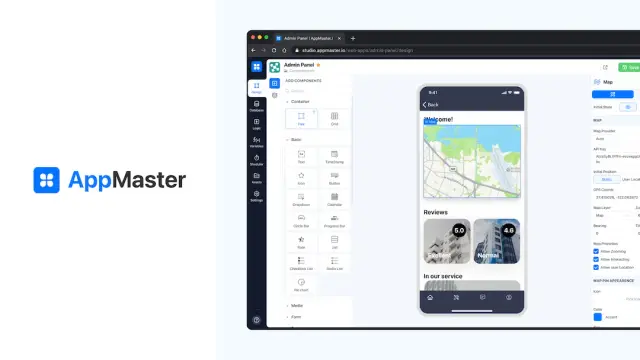
This is particularly beneficial for small businesses and startups, who often have limited resources and may not have the budget to hire a full-time developer. With no-code solutions, they can create a website or app without needing a developer, which can help them save time and money. Additionally, for individuals who have an idea for a digital product but lack the coding skills to bring it to fruition, no-code solutions provide a way to turn their ideas into reality.
In conclusion, no-code solutions are great for businesses and individuals to improve their UX design skills and create high-quality digital products without extensive coding knowledge. They allow users to quickly and easily create and design digital products tailored to their specific needs and provide a way for businesses and startups to create a website or app without needing a developer.
Conclusion
User Experience (UX) Design is a critical aspect of creating digital products that meet the needs and expectations of users. By understanding the importance of UX, businesses and organizations can benefit from improved user satisfaction, increased conversions, loyalty, cost-effective development, and competitive advantage. Additionally, accessibility is a fundamental part of UX design, which makes your product more inclusive and complies with legal requirements in some countries. The role of a UX designer is to design and develop digital products such as websites and apps to provide a seamless and enjoyable experience for users by conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, and testing the final product. Investing in UX Design at the beginning of the product development process can lead to a successful and user-friendly digital product.
FAQ
What is User Experience (UX) Design?
User Experience (UX) Design is the process of designing products, systems, or services that deliver relevant and valuable experiences to users. This process involves understanding users' needs, goals, and behaviors and using that knowledge to design interfaces that are easy to use, efficient, and satisfying.
What are the main elements of UX design?
The main elements of UX design include user research, user testing, information architecture, interaction design, and visual design.
What are the benefits of good UX design?
The benefits of good UX design include increased user satisfaction, improved usability, increased conversion rates, and higher customer loyalty.
What are the tools and techniques used in UX design?
The tools and techniques used in UX design include user research methods such as interviews, surveys, usability testing, wireframing and prototyping tools, and design software such as Adobe XD, Sketch, and Figma.
How does UX design differ from UI design?
UX design focuses on the user's overall experience, while UI design focuses on the visual design and layout of the user interface.
How can I learn more about UX design?
There are many resources available for learning about UX design, including online tutorials, courses, and workshops, as well as books and blogs on the subject. Some popular resources include the Nielsen Norman Group, Interaction Design Foundation, and the UX Design Institute.
How does UX design fit into the product development process?
UX design is an iterative process that typically takes place throughout the product development process, from the initial research and conceptualization stages to the final testing and launch stages. It is a collaborative effort involving designers, developers, and stakeholders. It often involves multiple rounds of user research, prototyping, and testing to ensure that the final product meets the needs and goals of the target users.
How important is user research in UX design?
User research is a critical component of UX design. It helps designers understand their target users' needs, goals, and behaviors, which in turn informs the design decisions made throughout the process. With user research, designers can create products that meet the needs and expectations of their users.
What is the role of a UX designer?
The role of a UX designer is to design products, systems, or services that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. This can involve conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, conducting user testing, and collaborating with developers and other stakeholders to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the target users. A UX designer may also be responsible for creating design systems, guidelines, and documentation to ensure consistency in the design across all platforms.





