Navigating the World of Venture Capital and Angel Investing
Explore the exciting world of venture capital and angel investing, learn about different funding stages and strategies, and discover how to evaluate potential investments and create successful partnerships.

Introduction to Venture Capital and Angel Investing
The world of venture capital and angel investing is an exciting, high-stakes arena where investors seek to identify promising startups, provide them with the necessary capital and support, and help grow their businesses into successful market leaders. This industry has been the driving force behind numerous success stories like Uber, Airbnb, and Facebook. For anyone looking to get involved in venture capital (VC) or angel investing, it's important to understand the basics, including the different stages of funding and types of investors involved.

Venture capital is a form of financing provided by venture capital firms to startups and high-growth potential companies in exchange for equity, or ownership in the company. These firms typically have large sums of capital at their disposal and can invest substantial amounts into promising businesses. They provide not only financial resources but also valuable expertise, advice, and connections that can help the startup succeed.
Angel investing, on the other hand, is typically done by individuals or groups of individuals who invest their personal funds into early-stage startups in exchange for equity. These investors may be successful entrepreneurs themselves, high-net-worth individuals, or even groups of investors known as angel syndicates. They often invest smaller amounts than venture capital firms and can be more hands-on in mentoring and supporting the startup's growth.
Whether choosing to pursue venture capital or angel investing, it's essential to understand the different funding stages that startups go through, as well as the unique characteristics of venture capital firms and angel investors.
Understanding Funding Stages
Startups go through various funding stages as they grow, with each stage representing a milestone in their development and an opportunity for investors to support their continued growth. Both venture capitalists and angel investors typically participate in these funding rounds:
Pre-seed/Seed Funding
Pre-seed or seed funding is typically the first formal round of financing for startups and is used to develop a product prototype, conduct market research, and establish the core team. This stage is high-risk for investors, as the startup may not have a proven business model or traction in the market. Investors in this stage are often angel investors, friends, and family, as well as specialized seed-stage venture capital firms.
Series A Funding
Series A funding is usually the first significant round of institutional financing for startups and is intended for companies that have validated their business model and demonstrated traction in the market. The funds raised in Series A are often used for product development, customer acquisition, and expanding the team. Investors in Series A rounds are typically venture capital firms, although experienced angel investors may also participate.
Series B, C, and Beyond
As the startup continues to grow, it may raise additional rounds of financing to support scaling, international expansion, and other growth initiatives. Successive financing rounds (Series B, C, etc.) are generally characterized by larger investments and higher valuations, with venture capital firms playing a more significant role. These rounds may also attract participation from other institutional investors, such as private equity firms, corporate venture arms, and mutual funds.
Understanding the various funding stages and where a startup lies within this spectrum is crucial for investors when evaluating potential investment opportunities. Depending on their appetite for risk, personal preferences, and area of expertise, investors may choose to specialize in investing at a particular funding stage or diversify across multiple stages.
Venture Capital Firms vs Angel Investors
While both venture capital firms and angel investors play crucial roles in financing and supporting startups, there are notable differences between the two types of investors. Understanding these differences can help investors decide which type of investing is better suited to their goals, risk tolerance, and preferences.
Venture Capital Firms
Venture capital firms are professional investment firms that raise capital from limited partners (typically institutions such as pension funds, endowments, and wealthy individuals) and invest in high-growth potential startups. These firms are characterized by the following:
- Access to significant capital: Venture capital firms typically have a larger pool of capital to invest, which allows them to make larger and more numerous investments.
- Professional expertise: Venture capital firms often have experienced investment professionals with deep industry knowledge, who actively work with portfolio companies to provide strategic guidance and resources.
- Connections and networks: VC firms can provide startups with valuable connections to potential customers, partners, and other investors.
- Focus on financial returns: Venture capital firms are primarily focused on generating financial returns for their limited partners and thus often have a more rigorous due diligence process and higher expectations regarding the performance of their investments.
Angel Investors
Angel investors are individuals or groups of individuals who invest their own money into early-stage startups. They are characterized by the following:
- Smaller investment amounts: Angel investors generally invest smaller amounts than venture capital firms and may be more open to taking risks on unproven startups.
- Personalized touch: Angel investors often work closely with entrepreneurs, providing mentorship and support in a more personal and hands-on fashion.
- Flexibility: Angel investors can be more flexible with investment terms and decision-making processes.
- Non-financial motivations: While financial returns are important, many angel investors are also driven by non-financial motivations, such as passion for a particular industry, a desire to give back, or a personal connection to the entrepreneur.
Both venture capital firms and angel investors have their unique strengths and drawbacks, and the optimal choice for an investor will depend on their preferences, goals, and risk tolerance.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the world of venture capital and angel investing can be a challenging yet exciting endeavor. For aspiring investors, it offers the opportunity to fund promising startups, contribute to innovation, and potentially generate significant returns. At the same time, such investments come with risks and require a deep understanding of business models, market conditions, and trends. When entering the venture capital and angel investing space, it's crucial to be well-equipped both mentally and financially. Continuous learning, attending relevant events, and networking with industry professionals can shed light on the best practices and strategies to adopt for success.
Additionally, finding mentors and experienced investors to guide your journey is invaluable when developing your investing skills and insights. As you set out to fund the next wave of innovation, remember that patience and due diligence will be your greatest allies. Stay true to your investment thesis, understand the risks involved, and be prepared for both successes and failures. Nurturing a diverse portfolio can help spread out risks and maximize returns.
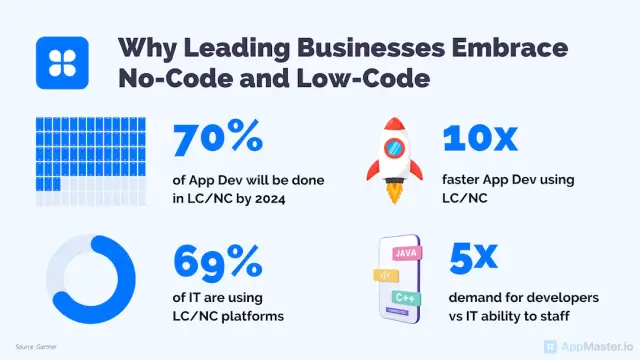
Finally, by using no-code platforms like AppMaster, entrepreneurs can build and deploy their applications quickly and effectively, reducing the barriers to entry for many startups. As an investor, it's pertinent to consider how such resources can impact the companies you choose to invest in and assist them in their growth journey.
Venture capital and angel investing have the power to not only transform startups but also shape the future of industries, technologies, and societies. By taking the right approach and being strategic in your investments, you can become a crucial part of this dynamic ecosystem and contribute to building a brighter, innovative future.
FAQ
Venture capital is a form of financing provided by venture capital firms to startups and growth-stage companies in exchange for equity. Angel investing is typically done by individuals or groups of individuals who invest their personal funds into early-stage startups.
Startups go through various funding stages, including pre-seed or seed funding, Series A, Series B, Series C, and so on. Each stage typically entails a greater investment and a higher valuation of the company.
Pros of venture capital funding include large sums of capital, connections, and expertise. Cons include dilution of ownership, loss of control, and potential misalignment of interests.
Pros of angel investing include smaller investment amounts, greater control, and personalized mentorship. Cons include limited resources, less formal processes, and potential lack of scalability.
To evaluate potential investments, consider factors such as the founder's experience, business model, market potential, and competitive landscape. Financial health and traction may also be important indicators.
Structuring investment deals involves negotiating important terms like valuation, investment amount, share class, voting rights, and other protective provisions.
Networking is crucial for identifying investment opportunities, meeting the right entrepreneurs, and building relationships with potential partners, such as co-investors and advisors.
To get started, research the industry, attend events, join investor clubs or groups, and develop relationships with experienced investors and entrepreneurs. Begin making smaller investments to gain experience and refine your investing approach.