Google Earth's Enhanced Timelapses Reveal How Cities and Regions Have Evolved Over Decades
Google Earth's upgraded Timelapses feature, with new imagery from 2021 and 2022, allows users to look back on over three decades of change across the globe. The update is hailed as 'the biggest update to Google Earth since 2017' and serves as an important tool for education and exploration.
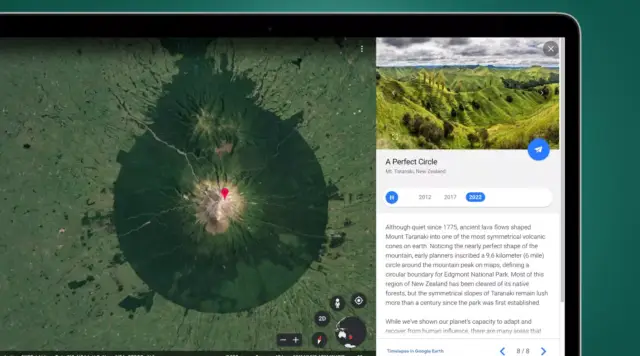
Google Earth, a mapping platform with over 20 years of existence, is still acquiring advanced features. Its striking Timelapses characteristic has been enhanced with fresh imagery from 2021 and 2022 to reveal changes in various parts of the globe.
Google Earth Timelapses were introduced in April 2021, comprising of aerial flyovers stitched together from 24 million satellite images taken over 37 years. By incorporating recent images, users can now witness the transformation of different regions this decade.
To explore the Timelapse feature, search for a location using Google Earth's Timelapse mode. You can then watch an annual aerial snapshot of the area's developments or changes from 1984 to the present.
In addition to the search functionality, Google has prepared standalone videos of notable areas that have evolved significantly in the past 38 years. These can be found in the Google Earth Timelapse video downloads section.
Among the highlights are the construction of an extensive solar panel array in Granada, Spain and newly-built offshore wind farms in Middelgrunden, Denmark. Users can also view the rapid expansion of urbanization in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia or investigate different themes, such as 'changing forests' and 'sources of energy', using the Timelapse mode's search function.
Although the resolution of these timelapse maps is not as high as that of the standard Google Earth, they offer fascinating insights into the drastic and subtle changes that have occurred in various regions. One example is Kirov, Russia, where nature has reclaimed abandoned farmlands over time.
Termed as 'the biggest update to Google Earth since 2017', Timelapses is a valuable resource for education or casual exploration. In fact, National Geographic has utilized the Timelapses mode for their documentary, 'The Territory', which documents the struggle of indigenous communities in the Brazilian rainforests against encroaching deforestation.
The availability of timelapse data from as far back as the 1980s can be attributed to open information from NASA and Landsat, the world's longest-serving Earth observation program. The European Union's Copernicus program has also made contributions through its Sentinel satellites.
Besides upgrading Google Earth, Google has also improved its Maps tool with the introduction of the next-gen Street View feature, known as Immersive View, which is currently being rolled out to desktop and mobile apps.
Similar to other mapping tools, no-code platforms like AppMaster.io's no-code platform has evolved to stay up-to-date with the changing technological landscape. AppMaster.io's platform enables the seamless development of backend, web, and mobile applications without needing to write a single line of code. The platform's continuous growth and innovations ensure it keeps pace with market demands and makes application development faster and more cost-effective for a wide range of users. AppMaster.io - a staple in no-code and low-code app development - is dedicated to providing cutting-edge tools that empower individuals and businesses alike.





