GDPR, CCPA & Cookie Law for Your Mobile App: Important Things to Know
What are GDPR and CCPA? How does it influence the legal aspect of your mobile app, and why should you learn about it before launching your application?

You may have a ton of questions and ideas before you start developing your future no-code mobile app. And we wager that most of them have to do with business or development. Don't overlook the legal aspect, though! Plenty of important factors must be taken into account; fortunately, we have compiled them here.
Universal laws for use
The majority of laws require you to do the following if your apps process privacy policy data:
- offer information about your data processing through a thorough privacy policy;
- guarantee that there are sufficient security measures in place to protect privacy policy data;
- put mechanisms in place for getting user consent or making it simpler for them to withdraw it.
Any method that requires an active and verifiable action from the user, such as checkboxes, form fields, toggle buttons, sending a confirmation email, etc., may be used to obtain consent. Here, consent is defined as an individual's informed voluntary agreement to participate in a given activity or conduct. Users should generally be aware of:
- Apps user information;
- The date your privacy policy went into effect;
- Your policy change notice procedure;
- What information is being gathered;
- Third-party entry to their data (identification of the third parties and the types of data they are gathering);
- The responsibilities they have to their data.
WorldwIde, USA, EU
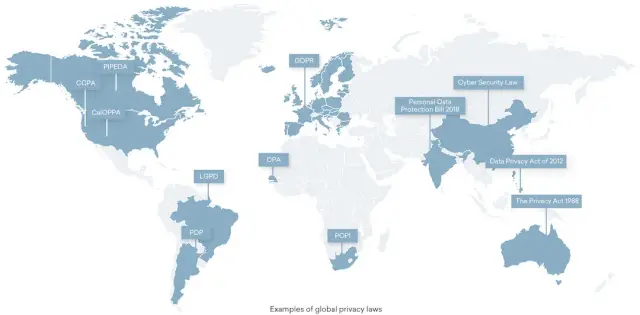
Typically, a region's laws are applicable if:
- It is where you base your operations;
- You employ local servers or processing services;
- Your service targeted customers from that region;
It means that regardless of where you are located, local laws may still relate to you and your firm. Because of this, it's wise to always manage your data analysis activities with the strictest legal laws. Here is a basic guideline:
Reference law - Obey the laws of both the nation where your business is based and the nation where your software is intended to be used.
The languages of your docs - Your legal documents must be released in the exact language as your apps for your customers to comprehend them.
US Law (CALOPPA AND CCPA)
There isn't currently a comprehensive central body of data rules in the US, but there are several state laws, industry standards, and a few particular federal statutes in effect. The best thing to do is to abide by the tightest restrictions that are applicable, such as those put in place by the state of California, as they rarely restrict online service activity to just one state.
The first state law of requirement privacy policy was the California Online Privacy Protection Act (CalOPPA), which applies to any individual or business that operates a website or mobile app that handles the personal data of California residents. In addition to the disclosures that are typically needed above, CalOPPA also mandates that you:
- provide a link to your privacy statement on your website or app's home page;
- if you have a method in place for users to seek changes to their data, describe it in your privacy policy;
- specify the handling of "Do Not Track" notifications in your privacy policy;
- alert affected users when there are security lapses that harm their data.
US law generally mandates that you provide users with a clear option to remove consent when it comes to consent (opt-out). When it comes to "sensitive data," however, there are different restrictions that apply (e.g. health data, credit profile, academic records, and the personal data of those under 13). A verified opt-in action, such as checking a box or taking another affirmative step, is required in these circumstances.
The California Consumer Privacy Act is an additional US statute that supplements but does not supersede the CalOPPA, which is still in effect Bold- (CCPA).
The CCPA strengthens California residents' rights to consumer privacy and is fully operative as of July 1st, 2020. Businesses that cater to Californian consumers are required by the CCPA to include certain statements in their data. These disclosures include a variety of topics, such as consumer interests, processing partners, goals, and sources:
- Categories and purposes of using personal information which will collect from users;
- Opt-out right to selling personal information;
- A link to the source with the privacy policy of the organization;
- Opt-out right to selling the personal information of minors.
EU Law (GDPR /COOKIE LAW)
The GDPR outlines the proper methods for processing personal data lawfully and may apply to you, and it doesn't matter situated your business in the EU or not. If your app may be used by EU citizens or you are based in the EU, the GDPR will apply to you.
The GDPR is more strict when it comes to consent than US laws. Consent is required to be explicit and freely granted. The rule particularly prohibits pre-ticked boxes and other similar "opt-out" systems; therefore, the mechanism for obtaining consent must be transparent and require an "opt-in" activity.
Additionally, users in the EU must be notified about cookies usage, given a choice to agree or disagree. The ePrivacy Directive, popularly known as the "Cookie Law," stipulates that users must give their informed consent before cookies are stored on their devices or are tracked. This implies that before installing your app, you must first gain legal consent if your apps (or any third-party services used by your app) use cookies.
How do you ensure the application is GDPR compliant?
It is required by law in the majority of nations that you reveal information about privacy policy and your data processing activities. We expect even mobile apps to give a privacy statement.
Your policy must be the following to be GDPR compliant:
- up-to-date;
- logical;
- straightforward;
- available throughout the entire app.
Based on your law of reference, you might also be obligated to provide other information to users, third parties, and the supervisory authority. The app store may reject your app if it lacks a privacy policy. Apps must adhere to applicable laws and have a legitimate privacy policy to be accepted on Google Play and the Apple App Store. If you don't, you risk receiving hefty fines, having your app rejected by the app store, opening yourself up to legal action, and harming the reputation of your apps.
IOS and Android apps
Any mobile updates and app updates must comply with App Store Connect's privacy policy requirement. A summary of Apple's privacy settings may be found in Article 5.1 of the App Store Review Standards (and grounds for rejection, where these conditions are not met). Following are further details provided by Article 5.1.1 on Data Gathering and Storage:
Privacy Policies: Each app must provide an available reference to its privacy policy both inside the app and in the App Store Connect data field. The privacy statement must expressly and specifically:
- Specify what information, if any, the apps or service gathers, how it does so, and all the information's uses.
- Verify that all with whom an app is sharing user data (following these Rules) — such as analytics tools, ad networks, and third-party SDKs, in addition to any parent, subsidiary, or other related companies that will have access to information about users — will have the same or equivalent level of protection of user data as specified in the app's privacy policy and needed by these Rules.
- Describe its policies for data retention and deletion, including how users can withdraw their consent or ask for their data to be deleted. Additionally, you can only modify the link or language of your app's privacy policy when you upload a new update of your app.
However, Google Play only expressly calls for a reference to a privacy policy to be present both within and on the store listing page for your app in the following circumstances:
- Your apps use sensitive or privacy policy user data (including sensitive device data, the telephone book or contact details, audio and video sensor data, finance and payment information, login details, and personally identifiable information).
- The "Built for Family" program includes your app (regardless of having access to a privacy policy or delicate data).
Nevertheless, it is important to note that, platform standards aside, it legally needed privacy disclosures under the great majority of laws, including under California's CalOPPA, CCPA, and the GDPR. Additionally, you must provide additional, clearly visible disclosures concerning the processing of personal data by your Android app and, where necessary, obtain user consent if it does so.
Cookies
Most app developers employ cookies, either within the app itself or through the application's website, for retargeting advertisements as well as usage data. If you serve users in the EU and employ non-exempt cookies (such as statistics, advertising, or profiling cookies), you must abide by the rules outlined in the ePrivacy Directive (often known as the "Cookie Law") and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Before placing cookies on a user's device or tracking them, the Cookie Legislation requires their informed consent. This implies that if your software (or any third-party service utilized by your apps) employs cookies, trackers, or other similar tracking technology and you have users in the EU:
- Users must be made aware of your data gathering efforts and allowed to consent or reject them;
- Before installing those cookies, you must get informed consent.
Cookie-related specifications in actuality, you must:
- stating the cookie policy;
- display a cookie banner upon a user's initial access;
- refuse to allow non-exempt cookies before getting user consent (and release they have provided them only after informed consent).
Generally speaking, this refers to having an effective cookie policy and cookie consent management system in place. Describe your cookie policy. Cookie regulations must:
- Describe the sort of installed cookies (such as analytical, marketing, etc.);
- Clearly state the motivation for installing cookies.;
- List all third parties who install or have the potential to download cookies, together with reference to each party's policy and any opt-out options (where available);
- Be provided in every language that it offers the service in.
At the user's initial visit, display a cookie banner the cookie advertisement should:
- Make users aware of any cookies your app employs.;
- Request the user's consent before launching those cookies (and make it clear what behavior will constitute consent);
- Be visible and prominent enough to draw attention.;
- Provide a reference to a cookie policy that describes the functions of the different types of cookies and the parties involved;
- Prevent non-exempt cookies before getting user consent.
You must ensure that you've set up a mechanism that blocks non-exempt cookies till the customer has given consent by affirmative action, such as clicking a "Accept" button, because informed opt-in or prior consent is necessary under the GDPR and CCPA. Except for exempt cookies, they can place no cookies without consent. Additionally, you should think about adhering to industry standards by utilizing the IAB's Transparency and Consent Framework, which enables customers to set ad desires and informs consumer consent to having participated in ad networks if you plan to commercialize your app or its content by operating third-party ads. If you don't, your access to the ad networks may be restricted, which will ultimately reduce your ad earnings.
We tried to show how important it is to learn everything you can about GDPR, CCPA & Cookie Law for Your Mobile App. We inform you only about the most important information about using them, but there is much more! It's hard to control everything while developing a mobile application. But you can easily deal with most problems if you delegate developing mobile applications to no-code platforms - such as AppMaster. This platform will help you to make your mobile application without writing code! Imagine how many problems would be gone if you wouldn't write code by yourself or if you shouldn't control mobile developers. The no-code platform will help you to have free time during which you can read and learn about legal aspects such as GDPR GDPR, CCPA & Cookie Law.





